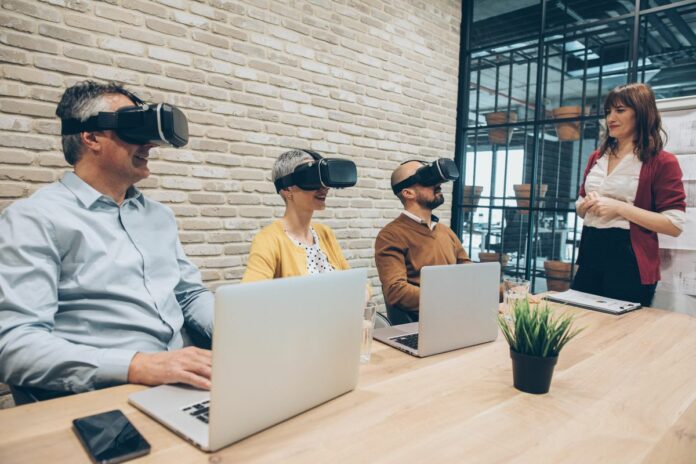
Developments in technology have a habit of making their way into the workplace; whether by improving efficiencies, saving costs, training employees, or boosting user experience. From the introduction of computers to offices in the 80s to the warm welcome the World Wide Web received in the 90s; the list of technological advancements is growing every day.
2020 has taught us all that we can learn and work remotely. Much of the success seen across working from home during the Coronavirus pandemic is owed to technology. Many large corporations, as well as small businesses, have realised that they can and should continue to work remotely. One of the very few concerns in doing so, is onboarding and training employees.
There’s also a clear indication that employees are more satisfied with their remote work conditions when they’ve received adequate remote training. Augmented reality is one of the most efficient and effective ways to train employees remotely.
Augmented reality (AR) is an emerging technology that has contributed to society in many different ways over the past decade. Applying AR in the workplace has become cost-effective and accessible – even for small businesses and SMEs. Not to be confused with virtual reality (VR) which requires larger and more sophisticated software and hardware, AR technology can be as discrete and as portable as a pair of eyeglasses.
Augmented reality wearables
The Internet of Things technology and connected devices that help build a more integrated and extended digital landscape is enhanced by the wearability of the device. As design patterns evolve dramatically, 2D screens are giving way to tools that use sensors, gestures, voice, and digital content to help people interact more seamlessly with the digital world.
When it comes to implementing AR wearables in the workplace; its application is virtually limitless. Questions of safety are particularly well-addressed. For instance, fieldworkers wear geofencing-enabled sensors that continuously track workers’ location and health.
AR wearables have the capacity to monitor and log an employee’s health (measured by their heart rate and body temperature), location, and the external environment that surrounds them. Real-time data on temperature, radiation and toxicity, for example, can alert any necessary individual if there are concerns.
In other words, the wearable AR-supported technology combined with geolocation helps to improve safety in remote workplaces where employees are likely to find themselves alone or in small teams in potentially harmful conditions.
AR Smartglasses for training remote employees
Many consider smart glasses to be the next biggest breakthrough of applied augmented reality that will infiltrate our daily lives. Putting useful real-time digital features in front of our eyes is now a reality and possesses great potential for giving new employees the best hands-free training in the remote workplace.
Apple is believed to be working on smart glasses that have AR at the center of its innovation. Its capability to merge the physical and digital worlds by overlaying data on the world around the wearer could provide great strides for trainee employees in any setting. For instance, those working with new machinery in the manufacturing industry would be able to keep their hands free and ready for action as they’re instructed through their smart lenses.
In other areas such as financial services, traders and portfolio managers can keep up on data including fluctuating stocks and market changes by having the real-time data displayed in their lenses.
Microsoft recently patented its AR glasses which allow the user to see objects through the fog. But this technology is by no means limited to this use. In the traditional employee training settings, the use of textbooks and verbal explanations as to how to handle a dangerous situation can only go so far. This new technology will allow new starters to get a head-start in real-life conditions without having to go through the motions of getting used to a particular working environment.
Types of AR wearable technology
There are typically two types of wearables that can be used as a tool in the remote workplace. The first, is with a headset, and the other – a more immersive and interactive session using smart glasses. Both increase trainee engagement, help to retain information, and allow training sessions to take place with real-time data without exhausting company resources.
AR headsets and training applications
The head-mounted tablet is a device that essentially connects to a helmet or har and allows the wearer to gain a picture-in-picture viewing of their peripheral vision. In the industrial world, this device is particularly useful for hands-free collaboration with connected experts – who can see your viewpoint from remote locations.
The device allows for remote inspections and relayed information to guide the wearer through their task in the real setting. It makes the head-mounted tablet an effective tool for the manufacturing, automotive, oil, and gas industries. It helps to virtually situate multiple experts in the same place with one trainee individual who might require guidance. It can help maintain awareness and avoid the trainee making mistakes on the job – ultimately saving costs in the long run.
The wearable AR device allows wearers to pull up data, documents and information in view of their eyes through voice control. This is particularly useful in the training setting where employees need not refer to textbooks or reach out directly to more experienced members of the team.
The head-mounted device has infinite merit across industrial applications where the workforce are expected to navigate between locations, systems, and settings.
AR smartglasses and training applications
Smartglasses are the most immersive, visually appealing, convenient, and portable wearable devices available on the market today. These tools allow the wearer to see an interactive digital overlay of graphical information in AR view. They can, of course, be used on the job in office environments and also in remote locations to support workers in the field to eliminate mistakes, reduce downtime and provide information on what to do in any given situation. If a person is working with computers and requires regular lenses to be worn at the same time, already, some smartglasses like Amazon Echo frames allow regular lenses to be installed, which means that workers won’t have to switch glasses all the time.
People who work extensively with computers should review and check their eye health regularly, and are often required to wear glasses while working in front of the computer. Hence, not only smart glasses are already adaptable for those that require wearing regular glasses, but can potentially be programmed to set automated reminders to take proper breaks and relieve eye strain.
They can be used to connect service teams with frontline technicians to ensure first-time fixes and prevent mistakes that might have otherwise happened. This type of device has been applied to the training sessions at Unilever – which was able to solve problems and reduce time by up to 50%. The company deployed the AR technology to help train new employees by their existing workforce, which led to an over 1700% increase in return on investment.
The downside to AR training tools
Smartglasses and even head-mounted displays are highly effective tools for giving trainee employees the information they need, when and where they need it. However, when it comes to the need to manipulate, engage with, and immerse yourself in a new environment – AR can only take its user so far. Virtual reality offers different interactivity levels which may be more suitable.
Nevertheless, AR wearables still aid on-site workers remotely by providing information and expert mentoring.